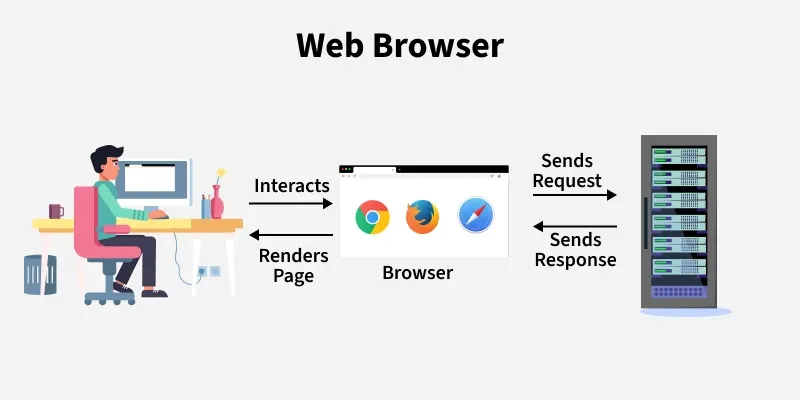
Express.js

1. Hello World
Create project, add package.json
mkdir myapp
cd myapp
npm init -yInstall express
npm install expressCreate index.js
const express = require("express");
const app = express();
const port = 3000;
app.get("/", (req, res) => {
res.send("Hello World!");
});
app.listen(port, () => {
console.log(`Listening on port ${port}`);
});Run
node index.js2. Express Generator CLI Help
Usage: express [options] [dir]
Options:
-h, --help output usage information
--version output version number
-e, --ejs add ejs engine support
--hbs add hbs engine support
--pug add pug engine support
-H, --hogan add hogan.js engine support
--no-view No view engine generated
-v, --view <engine> add view engine support
-c, --css <engine> add css support
--git add .gitignore
-f, --force force non-empty directoriesCreate Expess Project With Pug
express --view=pug myapp
cd myapp
npm install
DEBUG=myapp:* npm startFeatures
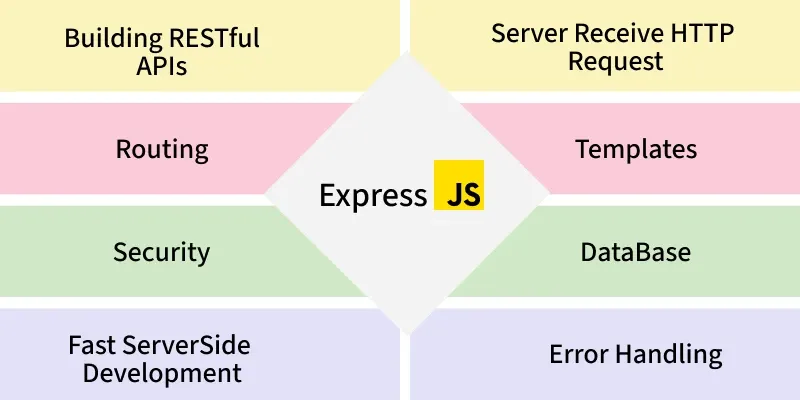
3. express() Core Functions
| Functions |
|---|
| express.json() |
| express.raw() |
| express.Router() |
| express.static() |
| express.text() |
| express.urlencoded() |
4. Router API
| Router Methods |
|---|
| router.all() |
| router.METHOD() |
| router.param() |
| router.route() |
| router.use() |
5. Application Example
var express = require("express");
var app = express();
console.dir(app.locals.title);
console.dir(app.locals.email);Application Attributes
| Property | Description |
|---|---|
| app.locals | Local variables |
| app.mountpath | Mount path |
Methods
App supports:
- app.all()
- app.delete()
- app.enable()
- app.disable()
- app.engine()
- app.get()
- app.listen()
- app.post()
- app.put()
- app.route()
- app.use().
.env
npm install dotenv
require("dotenv").config();
console.log("App Name:", process.env.APP_NAME);
console.log("Port:", process.env.PORT);Static files
const express = require("express");
const path = require("path");
const app = express();
// Serve static files from the 'public' folder
app.use(express.static(path.join(__dirname, "public")));
// Example route
app.get("/", (req, res) => {
res.sendFile(path.join(__dirname, "public/index.html"));
});
const PORT = 3000;
app.listen(PORT, () =>
console.log(`Server running on http://localhost:${PORT}`),
);6. Request Object
Attributes
- req.body
- req.params
- req.query
- req.method
- req.ip
- req.hostname
- req.xhr
- req.originalUrl
- req.cookies
Methods
- req.accepts()
- req.get()
- req.is()
- req.param()
- req.range()
route params
app.get("/users/:id", (req, res) => {
const userId = req.params.id;
res.send(`Fetching details for user ID: ${userId}`);
});Cross-Origin Resource Sharing (CORS)
const cors = require("cors");
app.use(cors()); // Allow cross-origin requests7. Response Object Example
app.get("/", function (req, res) {
console.dir(res.headersSent);
res.send("OK");
});Attributes
- res.app
- res.locals
- res.headersSent
Methods
- res.send() -> send a response
- res.json() -> Send a Json response
- res.redirect() -> Redirect the client to a different URL.
- res.render() -> Render a view template
- res.status() -> Set status code
- res.sendFile() -> Send a file as an octet stream.
- res.cookie() -> Send cookie to client
- res.clearCookie() -> Clear cookie on client
- res.download() -> Prompt a file download.
- res.end() -> End the response process manually.
8. Router Example
Middleware in Router
router.use(function (req, res, next) {
next();
});Route
router.get("/events", (req, res) => {
res.send("Events Route");
});9. Request Example
app.get("/user/:id", (req, res) => {
res.send("User " + req.params.id);
});File handling
const express = require('express');
const fs = require('fs');
const app = express();
app.use(express.json()); // To parse JSON bodies
// Writing to a file
app.post('/write', (req, res) => {
const { content } = req.body;
fs.writeFile('output.txt', content, (err) => {
if (err) {
return res.status(500).json({ error: 'Failed to write
file' });
}
res.json({ message: 'File written successfully!' });
});
});
const PORT = 3000;
app.listen(PORT, () => console.log(`Server running on
http://localhost:${PORT}`));Url Encoded for Forms
const express = require("express");
const app = express();
// Middleware to parse URL-encoded data
app.use(express.urlencoded({ extended: true }));
app.post("/form", (req, res) => {
console.log(req.body); // Parsed form data
res.send("Form data received");
});
const PORT = 3000;
app.listen(PORT, () =>
console.log(`Server running
on http://localhost:${PORT}`),
);10. Response Examples
res.end();
res.status(404).end();
res.json({ user: "tobi" });
res.status(500).json({ error: "message" });11. HTTP Methods
- app.get
The GET method is an HTTP request used by a client to retrieve data from the server. It takes two parameters: the URL to listen on and a callback function with req (client request) and res (server response) as arguments.
app.get("/users", (req, res) => {
res.send("GET Request - Fetching Users");
});- app.get – defines a GET route in Express.
- "URL" – the path the route listens to.
- (req, res) => {} – callback function where req is the client request and res is the server response.
- app.post
The POST method sends data from the client to the server, usually to store it in a database. It takes two parameters: the URL to listen on and a callback function with req (client request) and res (server response). The data sent is available in the request body and must be parsed as JSON.
app.post("/users", (req, res) => {
res.send("POST Request - Adding a User");
});- app.post – defines a POST route in Express.
- "URL" – the path the route listens to.
- (req, res) => {} – callback function where req contains client data and res sends the server response.
- app.put
The PUT method updates existing data in the database. It takes two parameters: the URL to listen on and a callback function with req (client request containing updated data in the body) and res (server response).
app.put("/users/:id", (req, res) => {
res.send(`PUT Request - Updating User with ID ${req.params.id}`);
});- app.put – defines a PUT route in Express.
- "URL" – the path the route listens to.
- (req, res) => {} – callback function where req contains the client’s updated data (usually in the body) and res sends the server response.
- app.delete
The DELETE method removes data from the database. It takes two parameters: the URL to listen on and a callback function with req (containing the ID of the item to delete in the body) and res (server response).
app.delete("/", (req, res) => {
res.send("DELETE request");
});- app.delete – defines a DELETE route in Express.
- "URL" – the path the route listens to.
- (req, res) => {} – callback function where req contains data (e.g., ID to delete) and res sends the server response.
- app.all
app.all("/secret", (req, res, next) => {
console.log("Access secret...");
next();
});12. Enable / Disable Features
app.disable("trust proxy");
app.disabled("trust proxy");
/*-----------------------------------------------------------------------------*/
app.enable("trust proxy");
app.enabled("trust proxy");13. app.listen()
const app = require("express")();
app.listen(3000);15. Middleware Example
function logOriginalUrl(req, res, next) {
console.log("URL:", req.originalUrl);
next();
}
function logMethod(req, res, next) {
console.log("Method:", req.method);
next();
}
const log = [logOriginalUrl, logMethod];
app.get("/user/:id", log, (req, res) => {
res.send("User Info");
});16. Body parser
- npm install body-parser
const bodyParser = require("body-parser");
app.use(bodyParser.json()); // Parse JSON bodies
app.post("/login", (req, res) => {
const { username, password } = req.body;
res.send(`Username: ${username}, Password: ${password}`);
});17. Template Engine (Pug)
Enable PUG
app.set("view engine", "pug");Create views/index.pug
html
head
title=title
body
h1=messageRender View
app.get("/", (req, res) => {
res.render("index", {
title: "Hey",
message: "Hello there!",
});
});18. cookies
const express = require("express");
const cookieParser = require("cookie-parser");
const app = express();
// Middleware to parse cookies
app.use(cookieParser());
// Route to set a cookie
app.get("/set-cookie", (req, res) => {
res.cookie("username", "user", { maxAge: 900000, httpOnly: true });
res.send("Cookie has been set");
});
// Route to read a cookie
app.get("/get-cookie", (req, res) => {
const cookies = req.cookies;
res.json({ cookies });
});
// Route to delete a cookie
app.get("/delete-cookie", (req, res) => {
res.clearCookie("username");
res.send("Cookie has been deleted");
});19 . Hashing password
const bcrypt = require("bcryptjs");
(async () => {
try {
const password = "mySecurePassword";
// Hash the password
const saltRounds = 10;
const hashedPassword = await bcrypt.hash(password, saltRounds);
console.log("Hashed Password:", hashedPassword);
// Verify the password
const isMatch = await bcrypt.compare(password, hashedPassword);
console.log("Password is valid:", isMatch); // true
} catch (error) {
console.error("Error:", error);
}
})();20. JWT
const jwt = require("jsonwebtoken");
// Secret key for signing the token
const secretKey = "your_secret_key";
// User data (could be from a database)
const user = {
id: 1,
username: "john_doe",
email: "john@example.com",
};
// Sign the JWT
const token = jwt.sign({ user }, secretKey, { expiresIn: "1h" });
console.log("Generated JWT:", token);
tokenss = jwt.verify(token, secretKey);
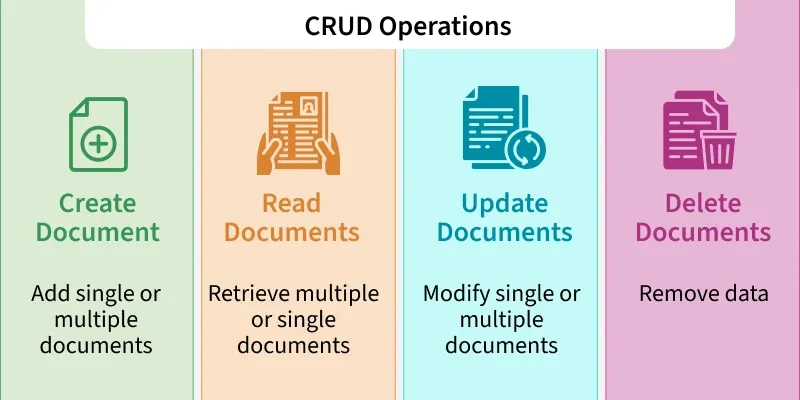
console.log(tokenss);21.Connect to MongoDB
- Create Schema
const mongoose = require("mongoose");
mongoose.connect("mongodb://localhost:27017/mydatabase");
// Define the schema for the 'User' model
const userSchema = new mongoose.Schema(
{
name: {
type: String,
required: true,
lowercase: true,
},
email: {
type: String,
required: true,
unique: true,
},
age: {
type: Number,
required: true,
},
},
{ timestamps: true },
);- Create the model based on the schema
const User = mongoose.model("User", userSchema);
// Create a new user
const newUser = new User({
name: "USER",
email: "john@exyyyample.com",
age: 30,
});
// Save the new user to the database
newUser
.save()
.then((user) => {
console.log("User created:", user);
console.log("User created and id is :", user._id);
})
.catch((err) => {
console.log("Error creating user:", err);
});- Delete the data By ID
async function deleteUserById(user) {
try {
const deletedUser = await User.deleteOne({ email: user });
if (deletedUser) {
console.log("Deleted User:", deletedUser);
} else {
console.log("User not found");
}
} catch (error) {
console.error("Error deleting user:", error);
}
}
// Call Function
deleteUserById("user@gmail.com");- Update one data
async function updateUserByEmail(email, newData) {
try {
const result = await User.updateOne({ email: email }, { $set:
newData });
console.log("Update Result:", result);
// You cannot access User._id here as `updateOne` does not
return the document itself
} catch (error) {
console.error("Error updating user:", error);
}
}
// Usage
updateUserByEmail("user@gmail.com", {
name: "John Updated",
age: 35,
email: "user1@gmail.com",
});- Update many data by age less than 35
async function updateMultipleUsers() {
try {
const result = await User.updateMany(
{ age: { $lt: 25 } },
{
$set: { age: 25 },
},
);
console.log("Update Result:", result);
} catch (error) {
console.error("Error updating users:", error);
}
}
// Usage
updateMultipleUsers();22. Morgan
Morgan.js is a middleware for Express.js that logs HTTP requests, making it easier to debug, monitor performance, and track user activity in your application. Morgan.js is an HTTP request logger middleware for Node.js and Express.js. It captures incoming HTTP requests and logs useful details such as:
- Request method (GET, POST, PUT, DELETE, etc.)
- Request URL (Path requested by the client)
- Response status code (200, 404, 500, etc.)
- Response time (Time taken to process the request)
- User agent : (Browser or client making the request)
Setup and Use Morgan in the Project
Here are the steps to set up Morgan in your project.
Step 1: Install Morgan
npm install morgan
Step 2: Verify Installation.
npm ls morgan
This command checks the installed version of Morgan in your project.
Step 3 Add Morgan to your Express Application
const morgan = require('morgan')
Step 4: Use Morgan Middleware
app.use(morgan('combined'));
- This line sets up Morgan to log HTTP requests using the 'combined' predefined format.
Example:
const express = require("express");
const morgan = require("morgan");
const app = express();
const PORT = 5000;
app.use(morgan("dev"));
app.get("/", (req, res) => {
res.send("Hello, World!");
});
app.listen(PORT, () => {
console.log(`Server running on PORT: \${PORT}`);
});Output :
GET /home 200 3.416 ms - 13
GET /login 200 2.416 ms - 22
==Predefined Formats in Morgan==
Morgan provides several predefined formats:
- combined: Standard Apache combined log output.
- common: Standard Apache common log output.
- dev: Concise output colored by response status for development use.
- short: Shorter than default, also including response time.
- tiny: The minimal output.
22.API Folders structures for vercel
Project_Folder/
│
├── api/ # Serverless function endpoints
│ ├── users/ # Group-related functions into folders
│ │ ├── get.js # Endpoint: /api/users/get
│ │ ├── create.js # Endpoint: /api/users/create
│ │ ├── update.js # Endpoint: /api/users/update
│ │ └── delete.js # Endpoint: /api/users/delete
│ │
│ └── index.js # Endpoint: /api (root API response)
│
├── utils/ # Utility functions for reusability
│ ├── db.js # Database connection setup
│ ├── responseHandler.js # Standardized response handling
│ └── validation.js # Input validation utilities
│
├── middlewares/ # Middleware for request preprocessing
│ ├── auth.js # Authentication middleware
│ ├── errorHandler.js # Error handling middleware
│ └── logger.js # Request logging middleware
│
├── vercel.json # Vercel configuration
└── README.md # Project documentation
vercel.json
- Add vercel.json Configuration
- Create a vercel.json file in your project root to tell Vercel how to handle the
- backend deployment.
{
"version": 2,
"builds": [
{
"src": "api/index.js",
"use": "@vercel/node"
}
],
"routes": [
{
"src": "/(.*)",
"dest": "api/index.js"
}
]
}