HTTP and Web
HTTP and Web
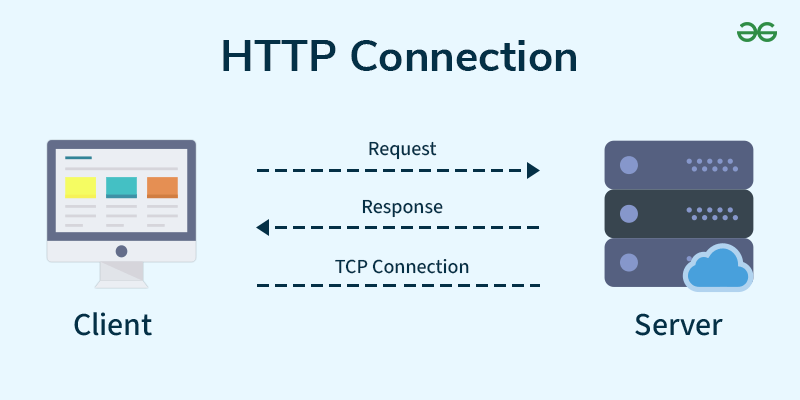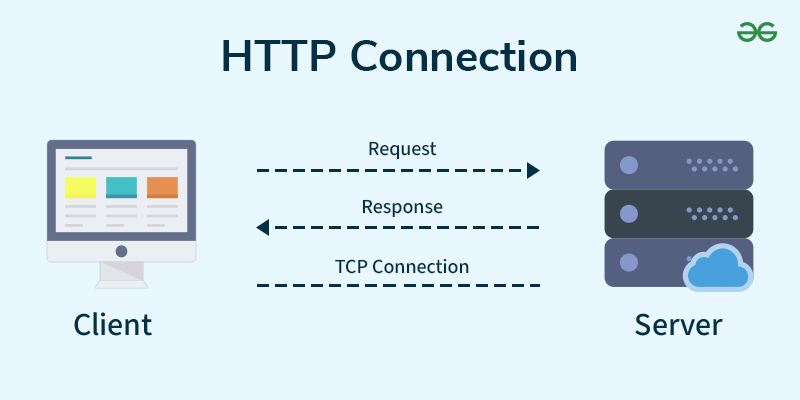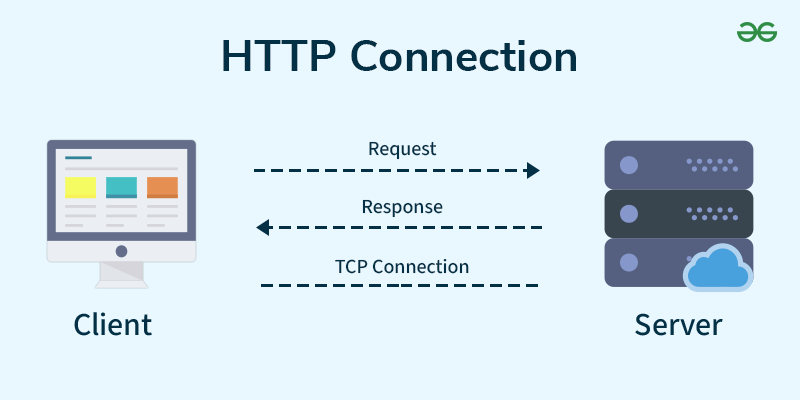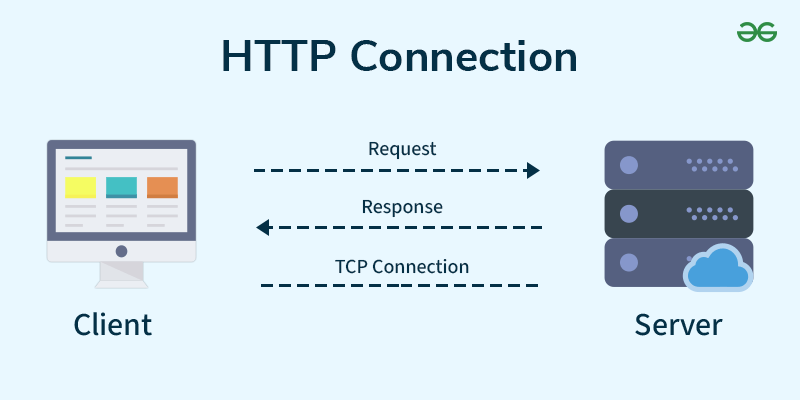
What is HTTP?
HTTP = Hyper Text Transfer Protocol
Used to transfer web pages.
- Stateless (no memory between requests)
- Uses port 80
- Text-based communication
HTTPS = Secure HTTP (encrypted)
Uses port 443
Client-Server Architecture
Client: Requests data
Server: Responds with data
Examples:
- Browser → Client
- Website → Server
HTTP Methods
| Method | Use |
|---|---|
| GET | Read data |
| POST | Send/Create data |
| PUT | Update data |
| DELETE | Delete data |
| PATCH | Partial update |
| HEAD | Header only |
| OPTIONS | Check available methods |
HTTP Status Codes
Success (2xx)
| Code | Meaning |
|---|---|
| 200 | OK — Successful |
| 201 | Created |
| 204 | No Content |
Redirect (3xx)
| Code | Meaning |
|---|---|
| 301 | Moved Permanently |
| 302 | Found |
| 304 | Not Modified |
Client Errors (4xx)
| Code | Meaning |
|---|---|
| 400 | Bad Request |
| 401 | Unauthorized |
| 403 | Forbidden |
| 404 | Not Found |
Server Errors (5xx)
| Code | Meaning |
|---|---|
| 500 | Internal Server Error |
| 502 | Bad Gateway |
| 503 | Service Unavailable |

URL Breakdown
Example:
https://www.example.com:443/home/index.html?user=1| Component | Value |
|---|---|
| Protocol | https |
| Subdomain | www |
| Domain | example.com |
| Port | 443 |
| Path | /home/index.html |
| Query | ?user=1 |
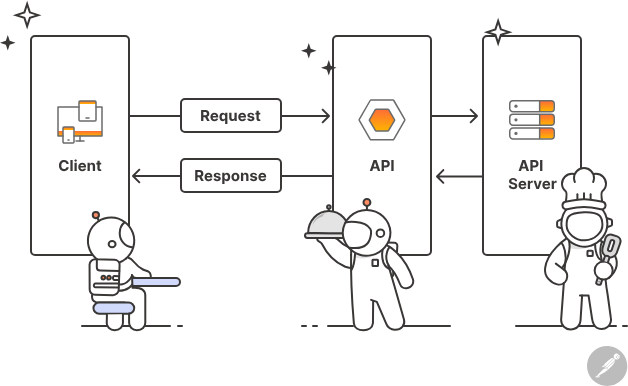
APIs
API = Application Programming Interface
Allows communication between applications.
Examples:
- Mobile app talking to server
- Weather app fetching weather data
Types of APIs
| Type | Description |
|---|---|
| REST | Resource-based, uses HTTP methods |
| GraphQL | Query language for APIs |
| SOAP | XML-based, more structured |
Cookies vs Sessions vs Local Storage
| Feature | Cookies | Sessions | Local Storage |
|---|---|---|---|
| Stored Where? | Browser | Server | Browser |
| Data Lifetime | Set by expiry | Until user logs out / expires | Until manually cleared |
| Size Limit | ~4KB | Depends on server | ~5–10MB |
| Security | Can be stolen if not secured | More secure | Less secure |
| Accessible By | Client + Server | Server only | Client (JavaScript) |
| Best For | Auth tokens, tracking, remember me | Login session, user identity | Preferences, theme, small app data |
| Automatically Sent to Server? | Yes (with every request) | No | No |
| Works Offline? | Yes | No | Yes |
What Happens When You Type google.com in Browser?
- DNS Resolution — Domain resolves to IP
- TCP Connection — Browser connects to server
- TLS Handshake — HTTPS encryption established
- HTTP Request — Browser sends GET request
- Server Response — Server returns HTML
- Page Rendering — Browser displays content
WebSocket
Allows real-time two-way communication.
Unlike HTTP which is request-response only, WebSocket keeps a persistent connection.
Used in:
- Chat applications
- Online games
- Live tracking
- Stock trading platforms
- Real-time notifications
Quick Reference
| Protocol | Port | Encrypted |
|---|---|---|
| HTTP | 80 | No |
| HTTPS | 443 | Yes |