Transport Layer Protocols
Transport Layer Protocols
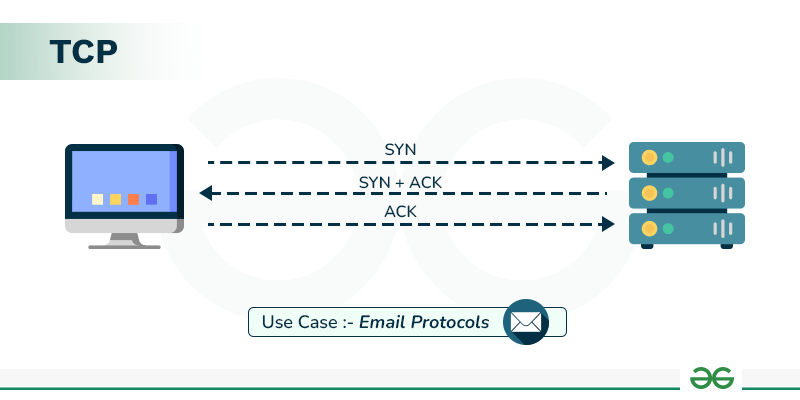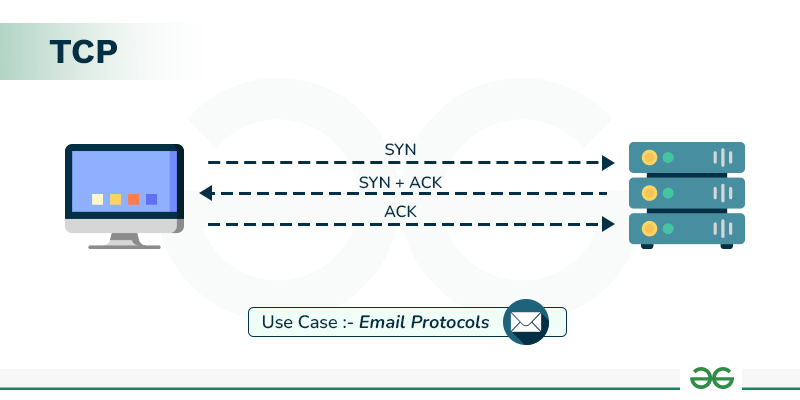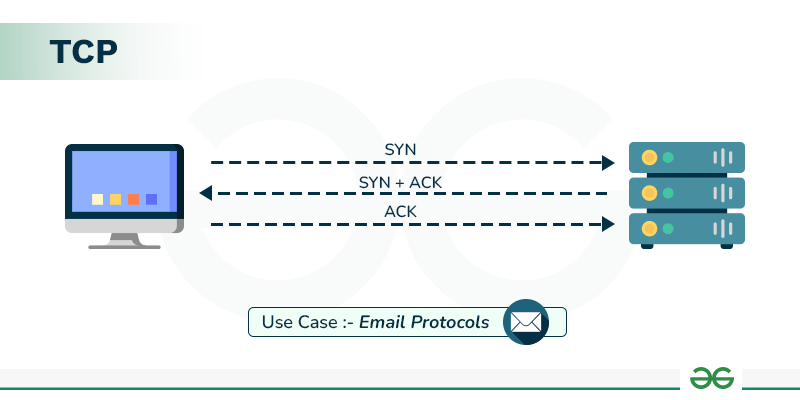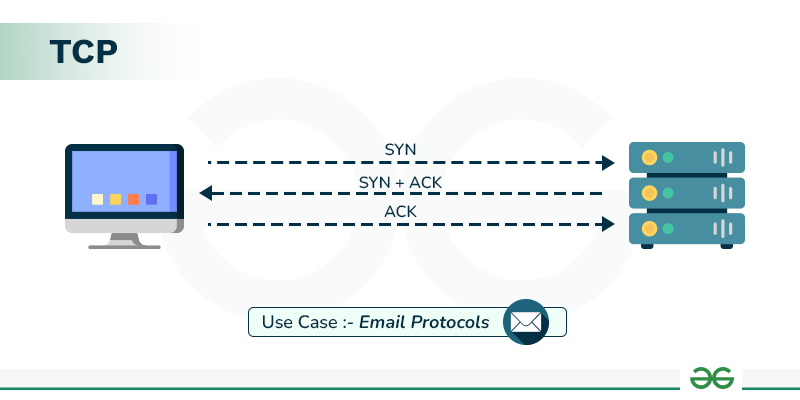
TCP (Transmission Control Protocol)
TCP is a connection-oriented protocol that ensures reliable data delivery.
Characteristics
- Reliable delivery
- Connection-based (3-way handshake)
- Ordered data transfer
- Error checking and correction
- Flow control
Use Cases
- Web browsing (HTTP/HTTPS)
- Email (SMTP, POP3, IMAP)
- File transfer (FTP)
- Remote access (SSH)
UDP (User Datagram Protocol)
UDP is a connectionless protocol that prioritizes speed over reliability.
Characteristics
- No connection establishment
- No guaranteed delivery
- No ordering of packets
- Lower latency
- Lightweight
Use Cases
- Online gaming
- Video streaming
- VoIP calls
- DNS queries
- Live broadcasts
TCP vs UDP Comparison
| Feature | TCP | UDP |
|---|---|---|
| Connection | Connection-oriented | Connectionless |
| Reliability | Reliable | Not reliable |
| Speed | Slower | Faster |
| Ordering | Ordered | No ordering |
| Error Checking | Yes + Correction | Yes (no correction) |
| Header Size | 20-60 bytes | 8 bytes |
| Overhead | High | Low |
| Use Case | Web, Email, File Transfer | Games, Streaming, VoIP |
Default Ports
Ports act as doorways for network communication. Each service uses a specific port number.
Well-Known Ports (0-1023)
| Service | Port | Protocol |
|---|---|---|
| HTTP | 80 | TCP |
| HTTPS | 443 | TCP |
| FTP Control | 21 | TCP |
| FTP Data | 20 | TCP |
| SSH | 22 | TCP |
| Telnet | 23 | TCP |
| SMTP | 25 | TCP |
| DNS | 53 | TCP/UDP |
| DHCP Server | 67 | UDP |
| DHCP Client | 68 | UDP |
| TFTP | 69 | UDP |
| POP3 | 110 | TCP |
| IMAP | 143 | TCP |
| SNMP | 161 | UDP |
Database Ports
| Service | Port |
|---|---|
| MySQL | 3306 |
| PostgreSQL | 5432 |
| MongoDB | 27017 |
| Redis | 6379 |
Secure Ports
| Service | Port |
|---|---|
| HTTPS | 443 |
| SMTPS (SSL) | 465 |
| SMTP (TLS) | 587 |
| IMAPS | 993 |
| POP3S | 995 |
Packets
Data in networks travels in small chunks called packets.
Packet Structure
A packet contains:
- Source IP — Where the packet comes from
- Destination IP — Where the packet is going
- Payload/Data — The actual content
- Headers — Control information
Packet Loss
Packets can be lost during transfer due to:
- Network congestion
- Hardware issues
- Weak signal
- Router buffer overflow
Bandwidth vs Latency
Bandwidth
- Definition: Maximum data transfer capacity of a network
- Measured in: Mbps, Gbps
- Analogy: Width of a highway (how many cars can pass)
Latency
- Definition: Delay time in data transfer
- Measured in: Milliseconds (ms)
- Analogy: Speed limit on the highway
Lower latency = Faster response
Quick Q&A
Q: When should I use TCP over UDP?
A: Use TCP when data accuracy is critical (file transfers, web pages, emails).
Q: When should I use UDP over TCP?
A: Use UDP when speed matters more than reliability (gaming, video calls, streaming).
Q: What is a socket?
A: A socket is the combination of IP address + Port number that identifies a specific connection endpoint.
Q: What is port forwarding?
A: Port forwarding exposes an internal service to the internet via router configuration.