DNS - Domain Name System
DNS - Domain Name System
DNS (Domain Name System) converts domain names to IP addresses.
Example:google.com → 142.250.183.14
Without DNS we would need to remember IP addresses for every website.
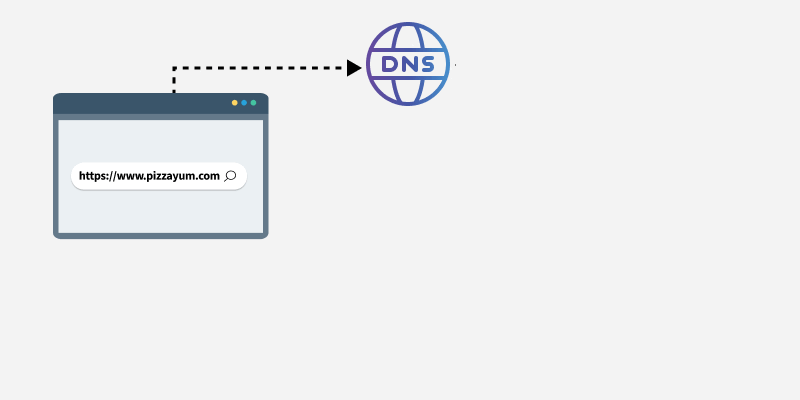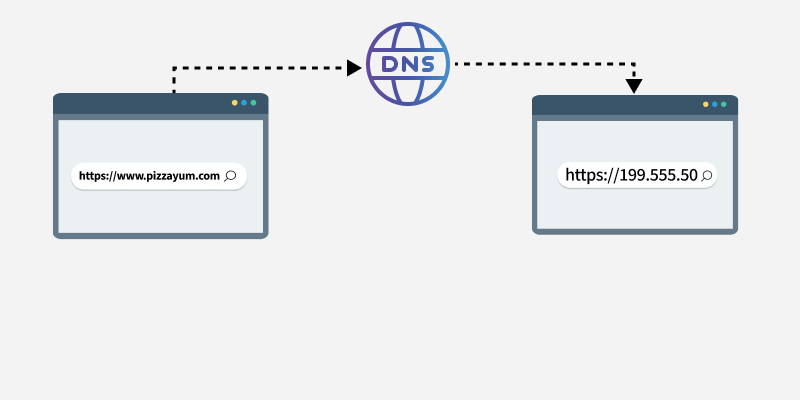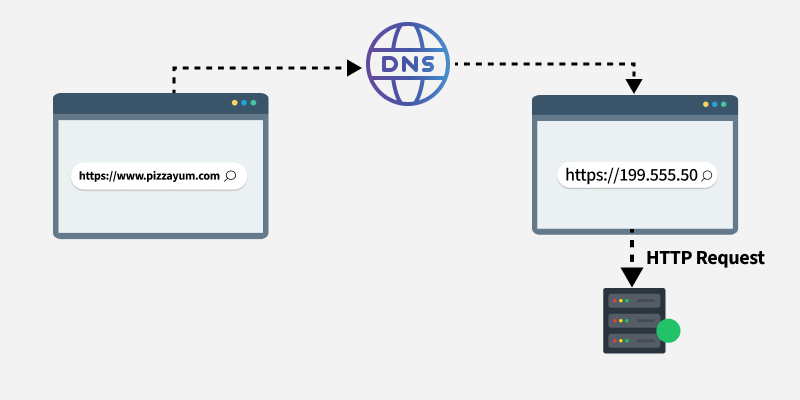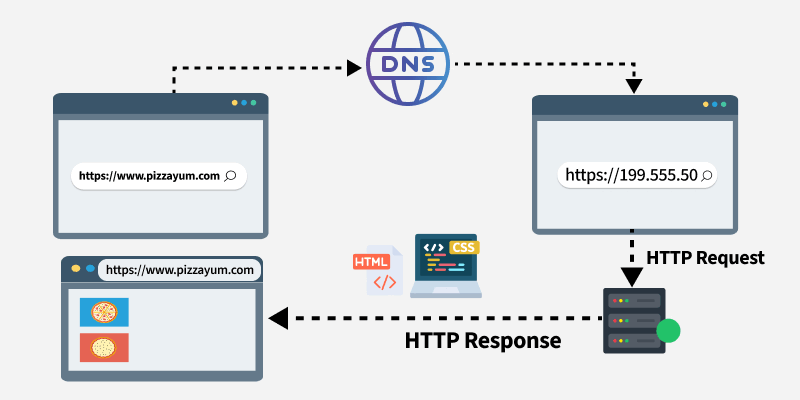
How DNS Works
- You type
google.comin your browser - Browser checks local cache
- If not found, asks DNS resolver
- DNS resolver queries root servers → TLD servers → Authoritative servers
- IP address is returned
- Browser connects to the IP
DNS Record Types
| Record Type | Purpose | Example |
|---|---|---|
| A | Maps domain to IPv4 address | example.com → 192.168.1.1 |
| AAAA | Maps domain to IPv6 address | example.com → 2001:db8::1 |
| CNAME | Maps domain to another domain | blog.example.com → medium.com |
| MX | Mail exchange server | example.com → mail.example.com |
| NS | Name server for the domain | example.com → ns1.example.com |
| TXT | Text records (SPF, verification) | example.com → "v=spf1..." |
| PTR | Reverse DNS lookup | 1.1.168.192 → example.com |
CNAME Records
CNAME = Canonical Name
Maps one domain name to another domain.
Example:
blog.example.com → example.medium.com
www.example.com → example.comUsed in:
- Hosting services
- CDNs
- Custom domains
- Subdomains pointing to external services
DNS Caching
DNS stores resolved results so next time lookup is faster.
Caching exists at:
- Browser cache
- Operating System cache
- Router cache
- ISP DNS servers
TTL (Time To Live):
- Determines how long a DNS record is cached
- Shorter TTL = faster propagation but more queries
- Longer TTL = fewer queries but slower updates
DNS Commands
Lookup domain:
nslookup google.comDetailed DNS query:
dig google.comCheck specific record type:
dig google.com MX
dig google.com AAAAFlush DNS cache (Linux):
sudo systemctl restart systemd-resolvedFlush DNS cache (Windows):
ipconfig /flushdnsDNS Security
| Threat | Description | Solution |
|---|---|---|
| DNS Spoofing | Fake DNS responses | DNSSEC |
| DNS Hijacking | Redirecting DNS queries | Secure DNS |
| Cache Poisoning | Injecting false records into cache | DNSSEC |
Secure DNS Options:
- DNS over HTTPS (DoH) - Port 443
- DNS over TLS (DoT) - Port 853
- DNSSEC - Cryptographic signatures
Popular DNS Servers
| Provider | Primary DNS | Secondary DNS |
|---|---|---|
| 8.8.8.8 | 8.8.4.4 | |
| Cloudflare | 1.1.1.1 | 1.0.0.1 |
| OpenDNS | 208.67.222.222 | 208.67.220.220 |
| Quad9 | 9.9.9.9 | 149.112.112.112 |
Quick Reference
- DNS Port: 53 (TCP/UDP)
- Purpose: Domain to IP translation
- Protocol: Application Layer
- Cache: Browser → OS → Router → ISP