IP Addressing
IP Addressing
An IP Address is a unique number assigned to every device in a network so it can be identified and communicate.
1. IP Address Basics
- Example:
192.168.1.10(IPv4) - Types:
- Private IP — used inside local networks
- Public IP — used on the internet
- Versions:
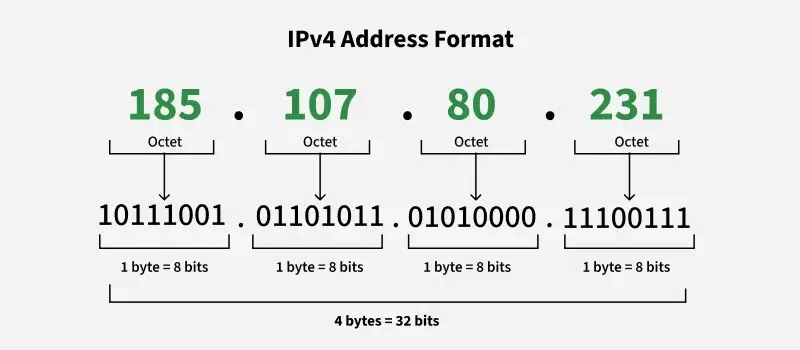
- IPv4 → 32-bit (like 192.168.1.1)
- IPv6 → 128-bit (like fe80::1)
2. Localhost (Loopback)
Used to refer to your own computer
127.0.0.1→ Localhost- Range:
127.0.0.0 – 127.255.255.255 - Used for:
- Testing
- Development
- No internet needed
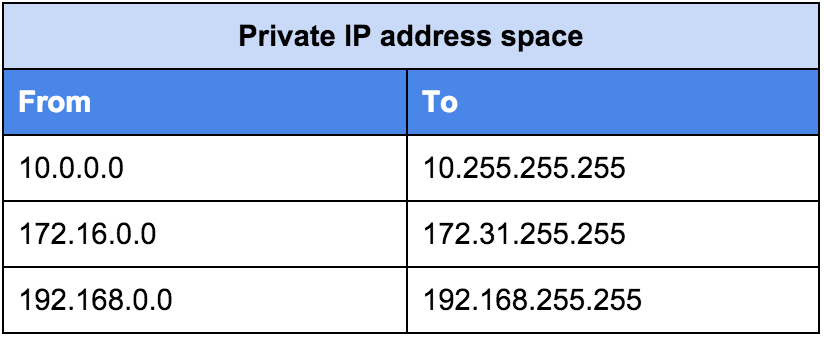
3. Private IP Addresses
Used inside homes, offices, LAN networks. Not accessible directly from internet.
Class A Private Range
Used in big networks
| Range | 10.0.0.0 – 10.255.255.255 |
|---|
Examples:
10.0.0.110.10.10.1010.1.1.1
Class B Private Range
Used in medium networks
| Range | 172.16.0.0 – 172.31.255.255 |
|---|
Examples:
172.16.0.1172.20.5.10172.31.100.50
❗ Only 172.16 → 172.31 are private. Other 172.x are public.
Class C Private Range
Most common in home WiFi
| Range | 192.168.0.0 – 192.168.255.255 |
|---|
Examples:
192.168.0.1192.168.1.1192.168.43.1(Hotspot)
4. Public IP
Used on the internet. Assigned by ISP.
Examples:
8.8.8.8(Google DNS)142.250.183.1452.95.245.123
Anyone on internet can reach (unless blocked).
5. Special IP Ranges
APIPA (Automatic Private IP)
Assigned when no DHCP / WiFi problem
| Range | 169.254.x.x |
|---|
Meaning:
- Network problem
- Failed to get IP
6. MAC Address
A MAC Address is a hardware identifier burned into the network card by the manufacturer.
| Feature | Description |
|---|---|
| Example | A4:B3:22:1F:9C:10 |
| Layer | Data Link Layer |
| Size | 48-bit address |
| Changes | Never (normally) |
Remember: MAC = Physical identity, IP = Logical identity
IP vs MAC
| Feature | IP Address | MAC Address |
|---|---|---|
| Type | Logical identifier | Physical identifier |
| Layer | Network Layer | Data Link Layer |
| Assigned by | Network/ISP | Manufacturer |
| Changes | Yes (dynamic) | No (hardware) |
7. Subnetting
Subnetting divides a large network into smaller networks.
Why Subnet?
- Better performance
- Improved security
- Efficient IP usage
Example
Network: 192.168.1.0/24
Subnetted into:
192.168.1.0/26192.168.1.64/26192.168.1.128/26192.168.1.192/26
8. CIDR Notation
CIDR = Classless Inter-Domain Routing
Represents network mask.
| CIDR | Subnet Mask | Hosts |
|---|---|---|
/24 |
255.255.255.0 | 254 |
/16 |
255.255.0.0 | 65,534 |
/32 |
255.255.255.255 | 1 (single IP) |
/8 |
255.0.0.0 | 16,777,214 |
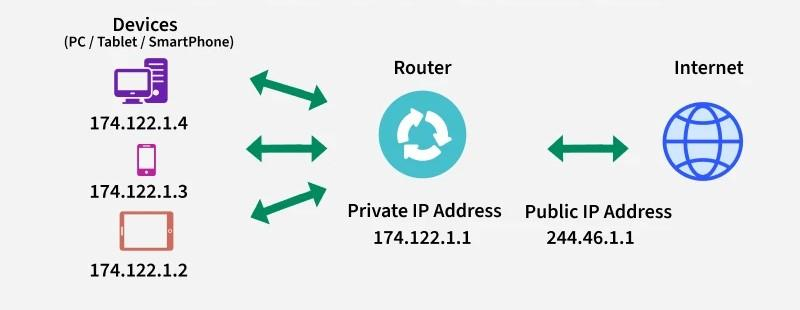
9. NAT (Network Address Translation)
NAT converts Private IP ↔ Public IP
Uses
- Security
- Limited IPv4 saving
- Home routers
Types of NAT
| Type | Description |
|---|---|
| Static NAT | One-to-one mapping |
| Dynamic NAT | Pool of public IPs |
| PAT | Port Address Translation (many-to-one) |
10. Useful Commands
Show IP Addresses
ip addrShow Neighbors (ARP Table)
ip neighShow Routing Table
ip routeFind Public IP
curl ifconfig.meForce IPv4 or IPv6
curl -4 ifconfig.me
curl -6 ifconfig.meQuick Reference
| IP Type | Range | Use Case |
|---|---|---|
| Class A Private | 10.0.0.0/8 | Large networks |
| Class B Private | 172.16.0.0/12 | Medium networks |
| Class C Private | 192.168.0.0/16 | Home/Small networks |
| Loopback | 127.0.0.0/8 | Local testing |
| APIPA | 169.254.0.0/16 | No DHCP available |